View Memory Mapped Files
O7Wqq.jpg' alt='View Memory Mapped Files' title='View Memory Mapped Files' />Virtual Machine files and settings explained VMDK, VMX, SWAP and more explained On Cloud 9. So Im currently going through all the notes Ive ever written on VMware VI and v. Sphere in preparation for my VCP5 exam and thought Id share them with you, many of you will know big chunks already, but for those who are new to VMware, looking to round out their knowledge or looking for revision for exams may find them useful. This post will go through the basic anatomy of a Virtual Machine, including the files its made up of, and the options available. VMware white paper 1. Introduction VMware ESX is a hypervisor designed to efficiently manage hardware resources including CPU, memory, storage, and network among. This site has moved this archive version may be out of date. Reliable updates may be found at httpb. Whenever I tried to copy 4 files into my bin folder, after stopping the main service, I am getting an error with one file TexteDll. The error is Cannot copy. Byte Buffers and NonHeap Memory. Most Java programs spend their time working with objects on the JVM heap, using getter and setter methods to retrieve or change the. This will not go into the detail of advanced parameters at this time. Some of this information was created some time ago, I have tried to update wherever possible but if you notice something incorrect please let me know and I will do my best to update it promptly. Files that make up a VMThese are the files that make up a VM, below will be a detailed description of each. VMX file Configuration. VMXF file Supplementational Configuration. VMDK Files Disk related files, includes. VMDK, delta. vmdk, rdm. VSWP File Memory overflow SWAP file. VMSD File Snapshot details. VMSS File Memory contents of suspended VMVMSN File Snapshot Files. NVRAM File BIOS file. Log files. VMX file. The VMX file is the primary configuration file a virtual machine. Every aspect of your virtual machine is detailed in the VMX file. Memory_Map.jpg/533865648/800x368/Memory_Map.jpg' alt='View Memory Mapped Files' title='View Memory Mapped Files' />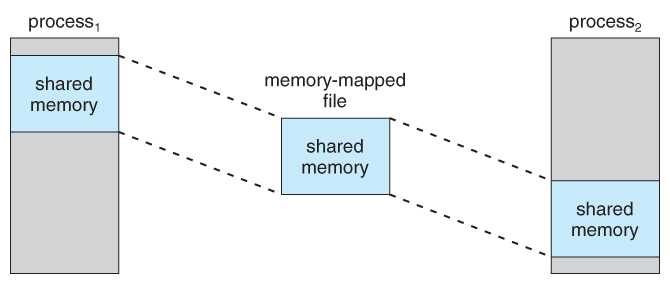 Any virtual hardware assigned to your virtual machine is present here. An example entry for a virtual floppy drive is outlined below floppy. Connected falsefloppy. Device trueEach time you create a new virtual machine using the New Virtual Machine Wizard, the VMX file is appended to with each question you answer regarding the guest operating system, disk sizes, and networking. Question Writer 4 Crack. Whenever you edit the settings of a virtual machine, this file is updated to reflect those changes. Things that are included in this file. Hardware configuration incl. What is Memory Forensics Study of data captured from memory of a target system Ideal analysis includes physical memory data from RAM as. Its name is kind of unique for something that shows system statistics top. It is a part of the procps package, a set of Linux utilities that provide system information. Or you can simply index the network files as a workaround. Add a nonindexed UNC as a library 1. Create a folder on your hard drive. Workbench User Guide Eclipse platform overview Getting started Basic tutorial The Workbench Editors and views Editors Views. View Memory Mapped Files' title='View Memory Mapped Files' />RAM, NICs, Hard drive and serialparallel port info,Advanced power and resource settings. VMware tools options. Power management options. Warning making direct changes to this file should be done with care, and either creating a backup or updating your resume should be undertaken before directly editing this file especially on production VMs. VMFX File. This file is a supplemental configuration file that is only retained for compatibility purposes with VM teaming in Workstation. VMDK Files. All virtual disks are made up of two files, a large data file equal to the size of the virtual disk and a small text disk descriptor file. The. vmdk file. Th descriptor file describes the size and geometry of the virtual disk file. The descriptor file also contains a pointer to the large data file as well as information on the virtual disks drive sectors, heads, cylinders and disk adapter type. The flat. vmdk file. This is the virtual disk data file that is created when you add a virtual hard drive to your VM that is not an RDM. One of these files is created for each virtual hard drive that a VM has configured. The size will vary based on the maximum size of the disk, and the type of provisioning used i. The delta. vmdk file. These virtual disk data files are only used when snapshots are created of a virtual machine. When a snapshot is created, all writes to the original flat. A delta file will be created for each snapshot that you create for a VM and their file names will be incremented numerically i. These files are automatically deleted when the snapshot is deleted after they are merged back into the original flat. The rdm. vmdk file. This is the mapping file for the RDM that manages mapping data for the RDM device. The mapping file is presented to the ESXi host as an ordinary disk file, available for the usual file system operations. However, to the virtual machine the storage virtualization layer presents the mapped device as a virtual SCSI device. The metadata in the mapping file includes the location of the mapped device name resolution and the locking state of the mapped device. If you do a directory listing you will see that these files will appear to take up the same amount of disk space on the VMFS volume as the actual size of the LUN that it is mapped to, but in reality they just appear that way and their size is very small. One of these files is created for each RDM that is created on a VM. VSWP file. At VM power on, a memory swap file is created, it is equal to the memory designated to the VM in its VM settings. If the ESXi host cannot provide sufficient memory to the VM, and Balooning can not be utilised to free memory then the host will use this file as memory overflow. VMSD file. A field used for storing information and metadata about the snapshots of a virtual machine. The snapshot information in this file consists of the name of the VMDK and VMSN file used by each snapshot, the display name and description, and the UID of the snapshot. VMSS File. This file is used when virtual machines are suspended and is used to preserve the memory contents of the VM so it can start up again where it left off. When a VM is brought out of a suspend state, the contents of this file are written back into the physical memory of a host server. The file is deleted at next VM Poweroff. VMSN file. This file is used with snapshots to store the state of a virtual machine when a snapshot is taken. A separate. vmsn file is created for every snapshot that is created on a VM and is automatically deleted when the snapshot is deleted. NVRAM File. This file contains the BIOS of the virtual machine. These are the files that are created to log information about the virtual machine and are oftentimes used for troubleshooting purposes. There will be a number of these files present in a VMs directory. The current log file is always named vmware. A new log file is created either when a VM is powered off and back on or if the log file reaches the maximum defined size limit. The amount of log files that are retained and the maximum size limits are both defined as VM advanced configuration parameters log. Size and log. keep. Old. VMware Options. General Options. View or modify the virtual machine name, check the location of the configuration file and the working location of the virtual machine, or change the guest operating system type. App Options. Enable or disable v. App functionality. When v. App is enabled, you can select an IP allocation policy and other configurations particular to v. Apps. VMware Tools. Manage the power controls for the virtual machine and run VMware Tools scripts. You can also upgrade VMware Tools during power cycling and synchronize guest time with the host. General Advanced Options. Advantages Conventional File Processing System. Disable acceleration and enable logging, debugging, and statistics. Add configuration parameters. Power Management. Manage guest power options. Suspend the virtual machine or leave the virtual machine powered on when you put the guest operating system into standby. CPUID Mask. Hide or expose the NXXD flag. Hiding the NXXD flag increases v. Motion compatibility between hosts. MemoryCPU Hotplug. Disable or enable CPU and memory hotplug. You can disable Memory or CPU hotplug if you do not want to add memory or processors accidentally while the virtual machine is running. Boot Options. Set the boot delay when powering on virtual machines or to force BIOS setup and configure failed boot recovery. Fibre Channel NPIVControl virtual machine access to LUNs on a per virtual machine basis.
Any virtual hardware assigned to your virtual machine is present here. An example entry for a virtual floppy drive is outlined below floppy. Connected falsefloppy. Device trueEach time you create a new virtual machine using the New Virtual Machine Wizard, the VMX file is appended to with each question you answer regarding the guest operating system, disk sizes, and networking. Question Writer 4 Crack. Whenever you edit the settings of a virtual machine, this file is updated to reflect those changes. Things that are included in this file. Hardware configuration incl. What is Memory Forensics Study of data captured from memory of a target system Ideal analysis includes physical memory data from RAM as. Its name is kind of unique for something that shows system statistics top. It is a part of the procps package, a set of Linux utilities that provide system information. Or you can simply index the network files as a workaround. Add a nonindexed UNC as a library 1. Create a folder on your hard drive. Workbench User Guide Eclipse platform overview Getting started Basic tutorial The Workbench Editors and views Editors Views. View Memory Mapped Files' title='View Memory Mapped Files' />RAM, NICs, Hard drive and serialparallel port info,Advanced power and resource settings. VMware tools options. Power management options. Warning making direct changes to this file should be done with care, and either creating a backup or updating your resume should be undertaken before directly editing this file especially on production VMs. VMFX File. This file is a supplemental configuration file that is only retained for compatibility purposes with VM teaming in Workstation. VMDK Files. All virtual disks are made up of two files, a large data file equal to the size of the virtual disk and a small text disk descriptor file. The. vmdk file. Th descriptor file describes the size and geometry of the virtual disk file. The descriptor file also contains a pointer to the large data file as well as information on the virtual disks drive sectors, heads, cylinders and disk adapter type. The flat. vmdk file. This is the virtual disk data file that is created when you add a virtual hard drive to your VM that is not an RDM. One of these files is created for each virtual hard drive that a VM has configured. The size will vary based on the maximum size of the disk, and the type of provisioning used i. The delta. vmdk file. These virtual disk data files are only used when snapshots are created of a virtual machine. When a snapshot is created, all writes to the original flat. A delta file will be created for each snapshot that you create for a VM and their file names will be incremented numerically i. These files are automatically deleted when the snapshot is deleted after they are merged back into the original flat. The rdm. vmdk file. This is the mapping file for the RDM that manages mapping data for the RDM device. The mapping file is presented to the ESXi host as an ordinary disk file, available for the usual file system operations. However, to the virtual machine the storage virtualization layer presents the mapped device as a virtual SCSI device. The metadata in the mapping file includes the location of the mapped device name resolution and the locking state of the mapped device. If you do a directory listing you will see that these files will appear to take up the same amount of disk space on the VMFS volume as the actual size of the LUN that it is mapped to, but in reality they just appear that way and their size is very small. One of these files is created for each RDM that is created on a VM. VSWP file. At VM power on, a memory swap file is created, it is equal to the memory designated to the VM in its VM settings. If the ESXi host cannot provide sufficient memory to the VM, and Balooning can not be utilised to free memory then the host will use this file as memory overflow. VMSD file. A field used for storing information and metadata about the snapshots of a virtual machine. The snapshot information in this file consists of the name of the VMDK and VMSN file used by each snapshot, the display name and description, and the UID of the snapshot. VMSS File. This file is used when virtual machines are suspended and is used to preserve the memory contents of the VM so it can start up again where it left off. When a VM is brought out of a suspend state, the contents of this file are written back into the physical memory of a host server. The file is deleted at next VM Poweroff. VMSN file. This file is used with snapshots to store the state of a virtual machine when a snapshot is taken. A separate. vmsn file is created for every snapshot that is created on a VM and is automatically deleted when the snapshot is deleted. NVRAM File. This file contains the BIOS of the virtual machine. These are the files that are created to log information about the virtual machine and are oftentimes used for troubleshooting purposes. There will be a number of these files present in a VMs directory. The current log file is always named vmware. A new log file is created either when a VM is powered off and back on or if the log file reaches the maximum defined size limit. The amount of log files that are retained and the maximum size limits are both defined as VM advanced configuration parameters log. Size and log. keep. Old. VMware Options. General Options. View or modify the virtual machine name, check the location of the configuration file and the working location of the virtual machine, or change the guest operating system type. App Options. Enable or disable v. App functionality. When v. App is enabled, you can select an IP allocation policy and other configurations particular to v. Apps. VMware Tools. Manage the power controls for the virtual machine and run VMware Tools scripts. You can also upgrade VMware Tools during power cycling and synchronize guest time with the host. General Advanced Options. Advantages Conventional File Processing System. Disable acceleration and enable logging, debugging, and statistics. Add configuration parameters. Power Management. Manage guest power options. Suspend the virtual machine or leave the virtual machine powered on when you put the guest operating system into standby. CPUID Mask. Hide or expose the NXXD flag. Hiding the NXXD flag increases v. Motion compatibility between hosts. MemoryCPU Hotplug. Disable or enable CPU and memory hotplug. You can disable Memory or CPU hotplug if you do not want to add memory or processors accidentally while the virtual machine is running. Boot Options. Set the boot delay when powering on virtual machines or to force BIOS setup and configure failed boot recovery. Fibre Channel NPIVControl virtual machine access to LUNs on a per virtual machine basis.